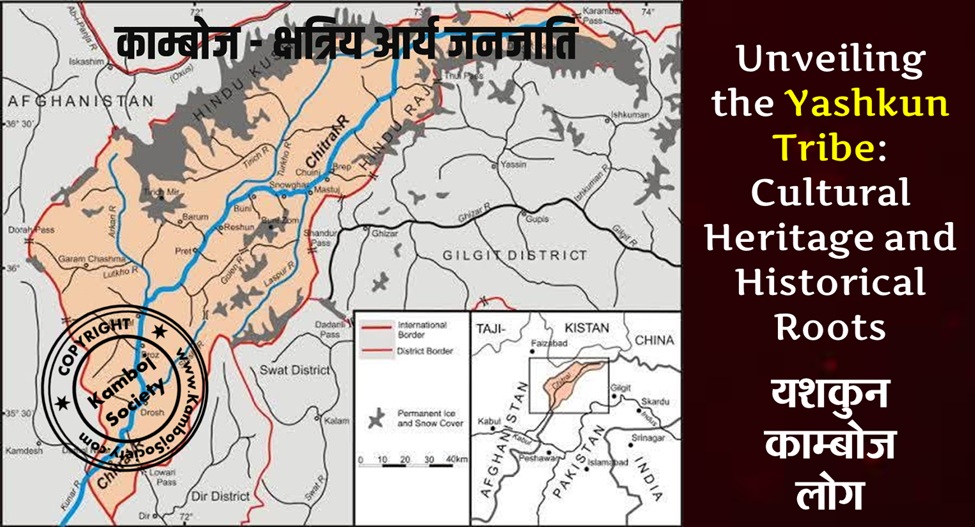
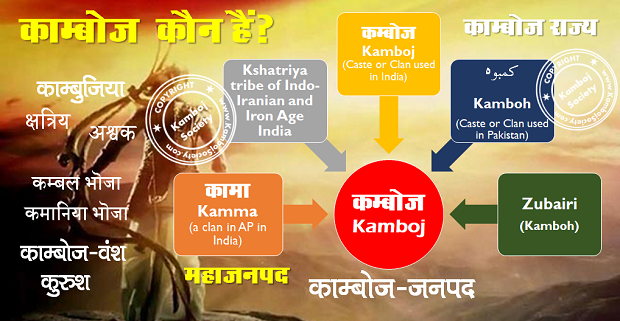
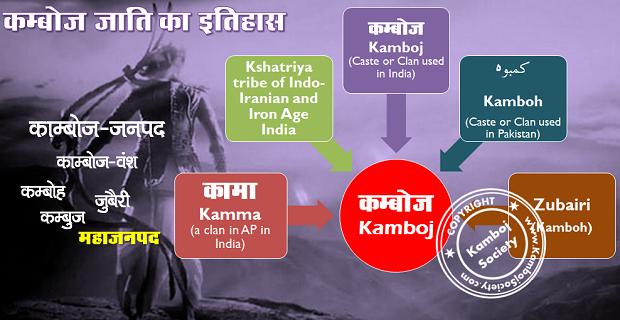
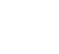Kamboja (Sanskrit: कम्बोज और काम्बोज ) was the ancient name of a country, and the Indo-Iranian (भारत-आर्यों) Kshatriya tribe (क्षत्रिय जनजाति), the Kambojas, settled therein. The country is listed as one of the sixteen Mahajanapadas or great nations in ancient Buddhist texts, and was located in the Uttarapatha in extreme north-west of the Indian sub-continent, contiguous to the kingdom of Gandhara. It initially included the Pamir Mountains|Pamirs, Badakshan, and territories as far as the Zeravshan valley in the doab of Oxus/Jaxartes. It approximated what is known today as the Galcha speaking region of Central Asia. Later, some sections of the trans-Hindu Kush (हिंदूकुश) Kambojas moved to southern side of the Hindukush and planted colony|colonies in Kunar, Swat (Pakistan)|Swat and as far as Rajauri in Kashmir. The Kambojas are attested to have had Indian as well as Iranian affinities Vedic Index I, p 138, Dr Macdonnel, Dr Keith. Ethnology of Ancient Bharata – 1970, p 107, Dr Ram Chandra Jain. The Journal of Asian Studies – 1956, p 384, Association for Asian Studies, Far Eastern Association (U.S.). Balocistan: siyasi kashmakash, muz?mirat va ruj?anat – 1989, p 2, Munir A?mad Marri. India as Known to Pa?ini: A Study of the Cultural Material in the Ash?adhyayi – 1953, p 49, Dr Vasudeva Sharana Agrawala. Afghanistan, p 58, W. K. Fraser, M. C. Gillet. Afghanistan, its People, its Society, its Culture, Donal N. Wilber, 1962, p 80, 311 etc..
Related Uses
- Camboja is the Portuguese language|Portuguese name for Cambodia.
- Kamboja is also the Indonesian name for Cambodia.
- Kamboja also refers to:
- The prince of the Kamboja Nation or TribePanini, IV.1.168-175..
- A descendant of the Kamboja KshatriyasPanini, IV.1.168-175..
- A horse raised and bred in ancient Kamboja (also Kambojaka, Kamboji) See: Halayudh Kosha''..
- An elephant native to, or coming from, Kamboja (also Kambu) See: Nanaratha.manjari''-421..
- ''Silver or gold native to, or coming from Kamboja (also Kambu).
- Name of a conch or shell native to Kamboja (also Kambu).
- Name of Supari or Punnag (Rottleria tinctoria) native to or coming from Kamboja see: Shabd.rattan.samanyavakosha''..
- Name of Somavalak or Karanj native to or coming from Kamboja See: Shabd.rattan.samanyavakosha''.
- Name of Ayurvedic herbal medicine Mashaparni and Hingparni, imported from Kamboja (also called Kamboji) See: Shabd.rattan.samanyavakosha''.
- Name of an ancient Raaga/Raagini (musical mode) originated in Kamboja country (??????? ???) (also called Kamboji, Kambhoji or Kambodi & Kambhodi). See Kambhoji
- A gold or silver bracelet, or bracelet in general (also Kambu).
- Name of a mountain located in ancient Kamboja (Afghanistan), famous for its Kambu or Kambuka silver''Kautiliya Arthashastra, 02.13.10. Sixty years of the Numismatic Society of India, 1910-1971, History and Presidential Address, Numismatic Society of India, 1973. Tribes Coins & Study, 1972, p 274, Dr Mahesh Kumar Sharma, University of Magadha. The Kambojas Through the Ages, 2005, p 76, K. S. Dardi. Kushana Silver Coinage, 1982, p 61, Bratindra Nath Mukherjee. Technology of Indian Coinage, 1988, p 72, P. K. D. Lee, Bratindra Nath Mukherjee, Indian Museum.. Silver mines of Anderab, Wakhan and other locations in Badakshan were noted during Arabic ruleGeographical and Economical Studies in the Mahabharata, Upayana Parava, Journal of U.P. Historical Research Society, Vol XVI, Part II, p 46, Dr. Moti Chandra.. Therefore, Kambu appears to be the name of a range of the Hindukush mountains in south-east Badakshan.
- Kamboji: the language of the ancient Kambojas.
Some Space/Time Variants of "Kamboja"
- Kaampoja (as in Mahabharata).
- Kaamboja (as in the Ramayana, Mahabharata and Vedic civilization|Vedic literature etc., hence Kaamboj). For few more variations of Kaamboja, see [https://www.msc.uky.edu/sohum/sanskrit/docs/sanshab.txt]
- Kambhoja (Southern Indian texts, as in Kautiliya's Arthashastra, hence Kambhoj).
- Kaambhoja (in Southern Indian versions of ancient Sanskrit texts, hence Kaambhoj).
- Kumbhoja (same as Kambhoja''; name of an ancient town in Maharashtra; also, the name of an ancient Kamboja sage referenced in some recensions of the Ramayana).
- Camboja (common variant spellings).
- Kambuja (as in dakshinatah Kambujaa.naam Vasisthaa.naam'': See Paraskara Grhya-Sutram 2.1.23).
- Kamvoja same as Kamboja.
- Kamvuja same as Kambuja.
- Kambuj (from Kambuja, like a Kamboj is from Kamboja).
- Kaanboja (a variant of Kamboja''; See Triya Chritra 217/verse 14 of Chritropakhyana of Dasam Granth; Hence Kaanboj. See also pages 21-23 of [https://www.gobindsadan.org/institute/dasam/pdf/v5_1.pdf]).
- Kanboj (variant of Kamboj).
- Kanbuj (as in a coin: Kharal-putras Kanbuj Raspag'': See Bharat ke Prachin Mudrank, by Swami Om Nand ji Sarasvati, 1973, Rohtak. Apparently Kanbuj is a variant of Kambuj/Kambuja, since m easily becomes n in Indo-Aryan languages, e.g Kambujiya = 'Kanbujiya).
- Cambuja (Variant spellings of Kambuja).
- Kamboza (As in the name of the Kamboza-thadi Palace of Bayintnaung, Myanmar).
- Kamodza, (as in Kamodza-radza referenced in the tenth century Sanskrit-Tibetan Formulary )Editor J. Hacklin, Formulair sanskrit-tibetain du xe siecle, 59, 1.16; See also Ancient Kamboja in Iran and Islam, p 66, Dr H. W. Bailey..
- Kamoz, Caumoje, Camoje (Pushtu names for a clan of the Siah-Posh Kafirs of the Hindukush).
- Kamtoz (also Kamtoj'''; Another Pushtu name for a Katir clan of the Siah-Posh Kafirs of the Hindukush). Said to be a variant of Kamboz).
- Kambu, as the name of an Asura, said to be a descendant of Hiranyakasipu. He falls in the fifth line of his generationThe Geographical Information in the Skanda-pura?a: Based on the Tirtha-yatra Portion, 1979, p 184, Umakant Thakur, Umesh Jha.
- Kambu, as in the name of an Asura clan, in conflict with Vedic Aryans, as referenced in Markendeya Purana Markendeya Purana 8.1-6., Devi MahatamDevi Mahatama 5.28.1-12..
- Kambu, as in the name of a learned prince who ventured into Mekong valley, married a local maiden Mera and laid the foundation of Kambuja (Kamboja) empire in Indo China.
- Kaaboja (See Luders' Inscriptions No 176, 472. It references one Kamboja Buddhist Bhikshu from Nandinagar making presents for a Buddhist Stupa)..
- Kabojha or Kabojhiya or Kabhojika (In ancient Sinhalese language|Sinhalese cave inscriptions) [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Talk:Kambojas/removed#KAMBOJA_SRI-LANKA_CONNECTIONS].
- Khamboja or Khaamboja (Sometimes) erroneous spellings of Kamboja or Kaamboja.
- Khambhoja or Khaambhoja (erroneous spellings of Kambhoja or Kaambhoja, southern Indian version).
- Khamboj (from Khamboja).
- Kamboda, Kambhoda (alternative name for Kamboja or Kambhoja Raga; also Kambodi or Kambhodi).
- Kambhoji (Southern Indian form of Kamboji).
- Kambojaka or Kambojika (Buddhist texts). Native of or loyal to Kamboja. A Kamboja daughter or maiden E.g: "A lovely girl in the flower of youth, robed in yellow, 'Kambhojika' (=Kambojika) of the beautiful hair, searching everywhere in the forest with her maids, the thought of her lover makes her weep with tenderness" (ref: Siva.tattva.ratnakara v. 6.8.99). See link: [https://www.loc.gov/folklife/guides/SouthAsian.html]..
- Kambhojaka or Kambhojika (Southern Indian spellings of Kambojika or Kambojaka).
- Kamboika, (from Kambojika== > Kamboyika== >Kamboika), Kamboi is the name of a "landlocked port" town in Gujarat. Tenth century Grant records of Chalukya rulers show it as Kamboika See Indian Antiquary VI, 1877, pp 191-92. The name is said to be a corruption of Pali Kambojika or Kambojaka (see above).
- Kapishi of Panini's Ashtadhyayi Sutra iv-2-99 of Ashtadhyayi (equivalent to Kamboja, as in the Ramayanamanjri by Pt Kshmendra of Kashmir.)
- Kau-fu (equivalent to Kambu, the Kamboja of Hiun Tsang) According to Dr J. W. McCrindle, Dr. R. K. Mukerjee, Dr. B. C. Law and others.
- Kieu-feou (name of Kamboja in the Chinese language|Chinese recension of Tathagata Grhya-Sutra (Ratnakutsangraha)).
- Kipin, ancient Chinese name for Kapisa (Kai-pi-shi(h)) of Hiuen Tsang Si-yu-ki, Kapishi (q.v.) of Panini Sutra iv-2-99 of Ashtadhyayi which according to scholars, is an alternative name for Kamboja See: Epigraphia Indica, Vol XIX-1, p 11, Indian Antiquary, 203, 1923, p 52; Indian historical quarterly, Vol XXV-3, 1949, pp 190-92; The Indian Historical Quarterly - Page 291 1963; Pre Aryan and Pre Dravidian in India, 1993, p 120, Sylvain L